GoRouter는 Flutter의 선언적 라우팅에 널리 사용되는 패키지입니다. Navigator 2.0 API를 기반으로 하며, 사용하기 쉬운 API를 바탕으로 딥 링크 및 기타 일반적인 탐색 시나리오를 지원합니다.
GoRouter를 사용할 때는 두 가지 별도의 옵션이 있습니다.
- go
- push
GoRouter 를 사용한 선언적 Routing
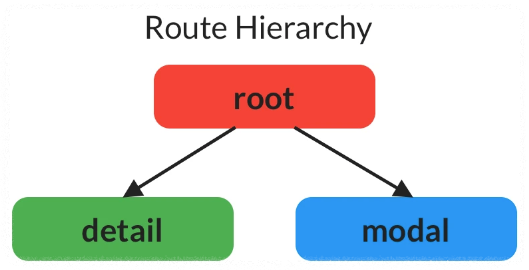
두 개의 하위 경로가 있는 하나의 상위 경로로 구성된 간단한 경로 계층 구조
GoRouter(
initialLocation: '/',
routes: [
// top-level route
GoRoute(
path: '/',
builder: (context, state) => const HomeScreen(),
routes: [
// one sub-route
GoRoute(
path: 'detail',
builder: (context, state) => const DetailScreen(),
),
// another sub-route
GoRoute(
path: 'modal',
pageBuilder: (context, state) => const MaterialPage(
fullscreenDialog: true,
child: ModalScreen(),
),
)
],
),
],
)
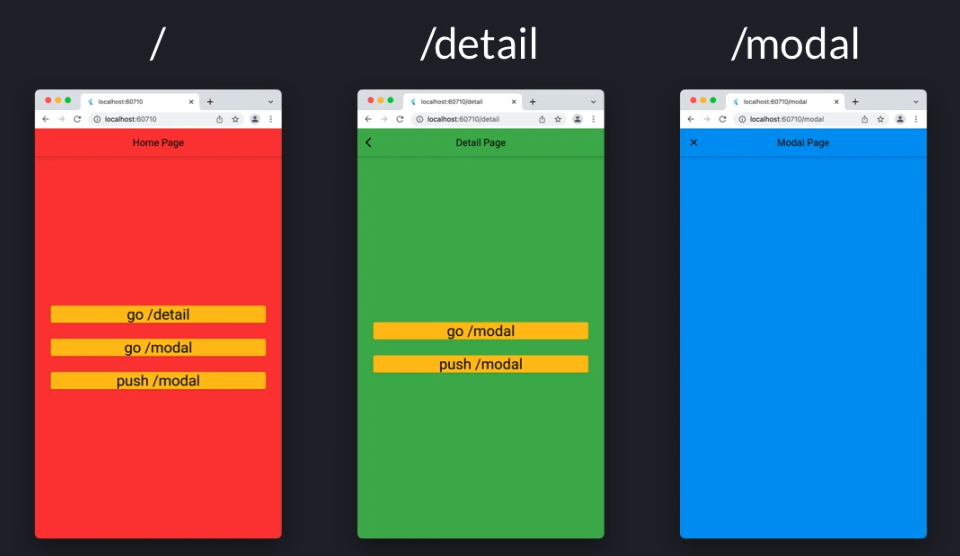
HomePage 에서 탐색
HomeScreen에 다음과 같이 콜백이 정의되어 있고, 세 개의 버튼이 있는 간단한 페이지에 있다고 가정해 보겠습니다.
// onPressed callback for the first button
context.go('/detail'),
// onPressed callback for the second button
context.push('/detail'),
// onPressed callback for the third button
context.go('/modal'),HomeScreen에서 이동 시,
첫 번째와 두 번째 콜백은 동일한 대상 위치 ( /detail )를 가지므로 결과적으로 동일한 방식으로 동작합니다.
즉 두 경우 모두, 탐색 스택에 ( home → Detail ) 이 상태로 있게 됩니다 .
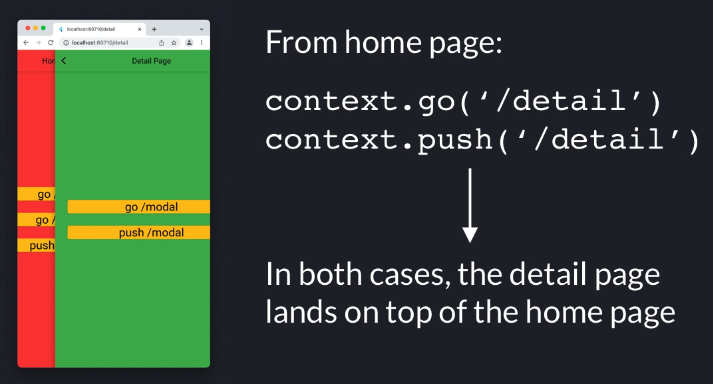
Go와 Push 의 차이점
이제 Detail 페이지에서 다음 두 가지 방법 으로 이동할 수 있습니다 .
// onPressed callback for the first button
context.go('/modal'),
// onPressed callback for the second button
context.push('/modal'),
응? 이번엔 결과가 다르다.
Detail 페이지에서 이동시
- go를 사용하면 Home Page 상단에 Model 페이지가 표시됩니다.
- push를 사용하면 Detail Page 상단에 Model 페이지가 표시됩니다.
위의 내용을 Page Stack 형식으로 표현하면
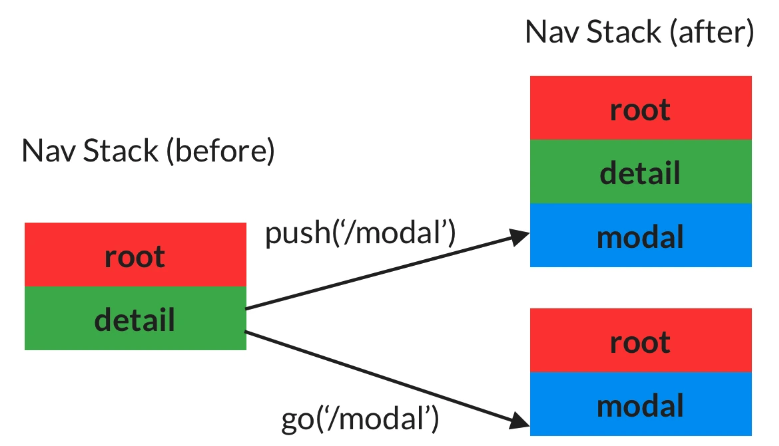
Detail 페이지에서 context.go('/modal')의 행동은
/modal은 /detail의 하위 경로가 아니므로 이전 경로( /detail) 를 버리고, Go의 대상 경로( /modal)로 점프하기 때문입니다.
=> go를 통해 가고자 하는 경로가 해당 위치의 하위 경로가 아니면,
이전 경로를 버리고, 점프!!
아래그림처럼 modal 은 detail 의 하위가 아니다.
Detail 페이지에서 context.push('/modal')의 행동은
push 는 항상 기존 경로 위에 대상 경로를 추가하여 탐색 스택을 유지합니다. (가장 일반적으로 우리가 알고 있는 이동방식)
다음은 이 동작을 보여주는 짧은 비디오입니다.

'Flutter' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Riverpod : 리버팟 (0) | 2024.04.01 |
|---|---|
| 빈 화면 터치. 키보드(자판) 숨기기 (0) | 2024.02.24 |
